You might have heard of CRUD. It's a concept of data manipulation which stands for:
- C: Create
- R: Read
- U: Update
- D: Delete
Which these four steps, we are generally able to create complete applications.
We'll learn how to handle CRUD operations on a Prisma database for today's article while using Fastify as our server. This way, the end-user will perform specific requests to the API endpoint, which will handle the CRUD operations.
Setting up the framework
We won't be making this project from scratch. If you are interested in setting up Prisma, check out this article.
In this article, we created two models, the User and the Hobby model.
A user can have multiple hobbies, so let's use this knowledge to enable our CRUD operations.
If you like to follow along, download the following GitHub repo.
The very first thing we'll want to do is install Fastify.
npm i fastify
I've also taken the liberty to add a start script for our application in the package.json file.
"scripts": {
"start": "ts-node index.ts",
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
Then let's change our index.ts file to run a primary Fastify server.
import fastify from 'fastify';
import {PrismaClient} from '@prisma/client';
const prisma = new PrismaClient();
const app = fastify();
// Todo: Create the routes
app.listen(3000);
In between, we'll start by adding our routes.
Creating the read routes
First up is a GET (read) route.
We want to retrieve all users with their hobbies by requesting the users endpoint.
app.get('/users', async (request, reply) => {
const allUsersAndHobbies = await prisma.user.findMany({
include: {
hobbies: true,
},
});
reply.send(allUsersAndHobbies);
});
Let's try it out to see if we are on the right track.
Run the startup script: npm run start.
Now open up your favorite API client and paste the URL in the bar http://localhost:3000/users.
Note: You can also use your browser for the get requests.
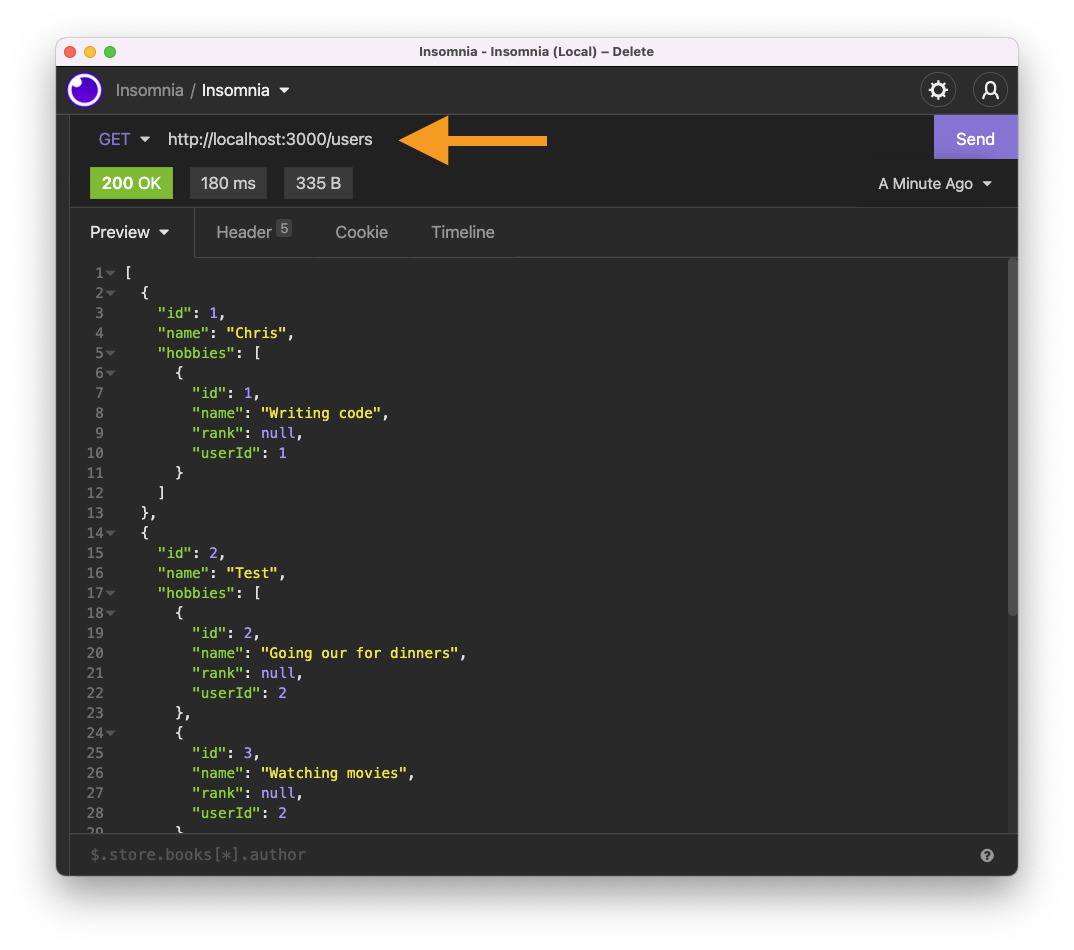
Alright, that is the first element done. There is, however, also the option to read just one user. We can leverage the Fastify params option for this.
app.get <
{Params: IByIdParam} >
('/user/:id',
async (request, reply) => {
const {id} = request.params;
const user = await prisma.user.findUnique({
where: {id: Number(id)},
include: {
hobbies: true,
},
});
reply.send(user);
});
You may have noticed I'm using a definition here to define what the Params look like.
This is because the typescript version of Fastify doesn't know wha5t kind of params to expect.
The interface I created looks like this:
interface IByIdParam {
id: number;
}
Now we can try and retrieve only the user with ID 1.
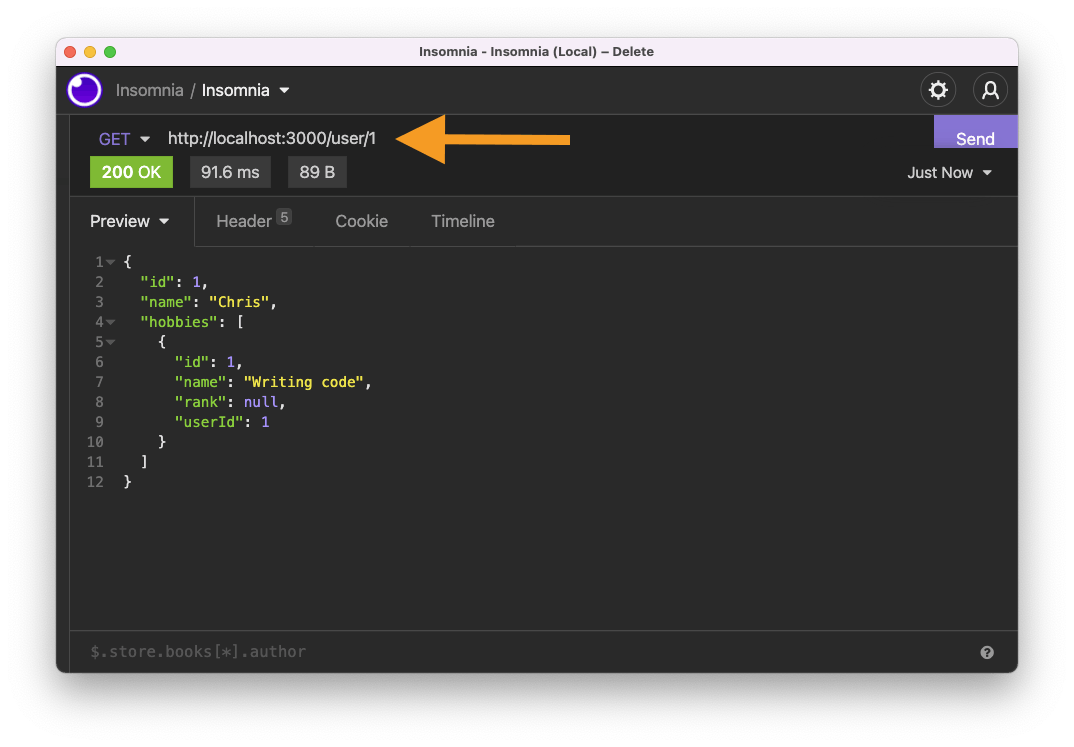
Amazing, this seems to work perfectly.
Create routes
The next thing on our list is to create new rows in our database.
For this, we use the POST request.
app.post <
{Body: IUserBodyParam} >
('/user',
async (request, reply) => {
const {name, hobbies} = request.body;
const user = await prisma.user.create({
data: {
name,
hobbies: {
create: hobbies.split(';').map((hobby) => ({
name: hobby,
})),
},
},
});
reply.send(user);
});
You see, we leverage the request body here, and as with the Params, Fastify does not know what our body will look like, so let's define the interface.
interface IUserBodyParam {
name: string;
hobbies: string;
}
As you can see, it accepts two strings, the name, and the hobbies.
The hobbies for the user will be a string delimited by a ; sign.
Let's say we push the following data:
{
"hobbies": "Surfing;Cooking",
"name": "Chris"
}
This will map into the following request:
const user = await prisma.user.create({
data: {
name,
hobbies: {
create: [{name: 'Surfing'}, {name: 'Cooking'}],
},
},
});
Let's try it out and see what happens.
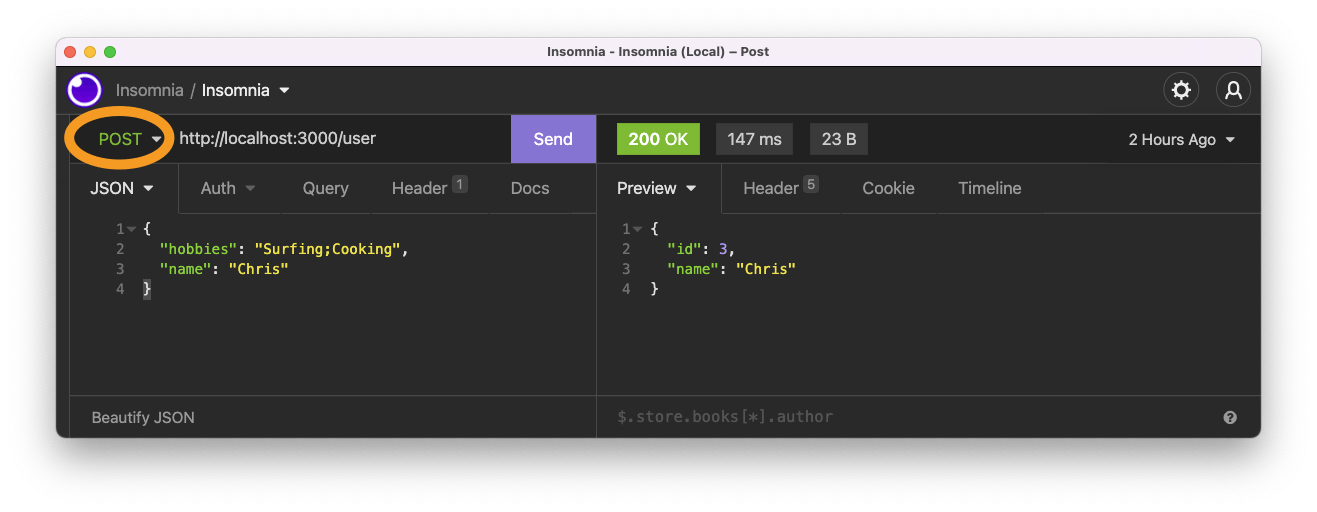
Nice, another one done.
Update a record
Oops, we made a mistake. We set the wrong name for a user. How can we update this?
We can leverage the PUT command and make an update route.
app.put<{ Body: IUserBodyParam; Params: IByIdParam }>(
'/user/:id',
async (request, reply) => {
const { id } = request.params;
const { name } = request.body;
const user = await prisma.user.update({
where: { id: Number(id) },
data: {
name,
},
});
reply.send(user);
}
);
As you can see, this route leverages both the body and the Params as we need to know the user's new name and ID.
Then we use the Prisma update query to update the user's name with this specific ID.
Let's try it out and see what happens.
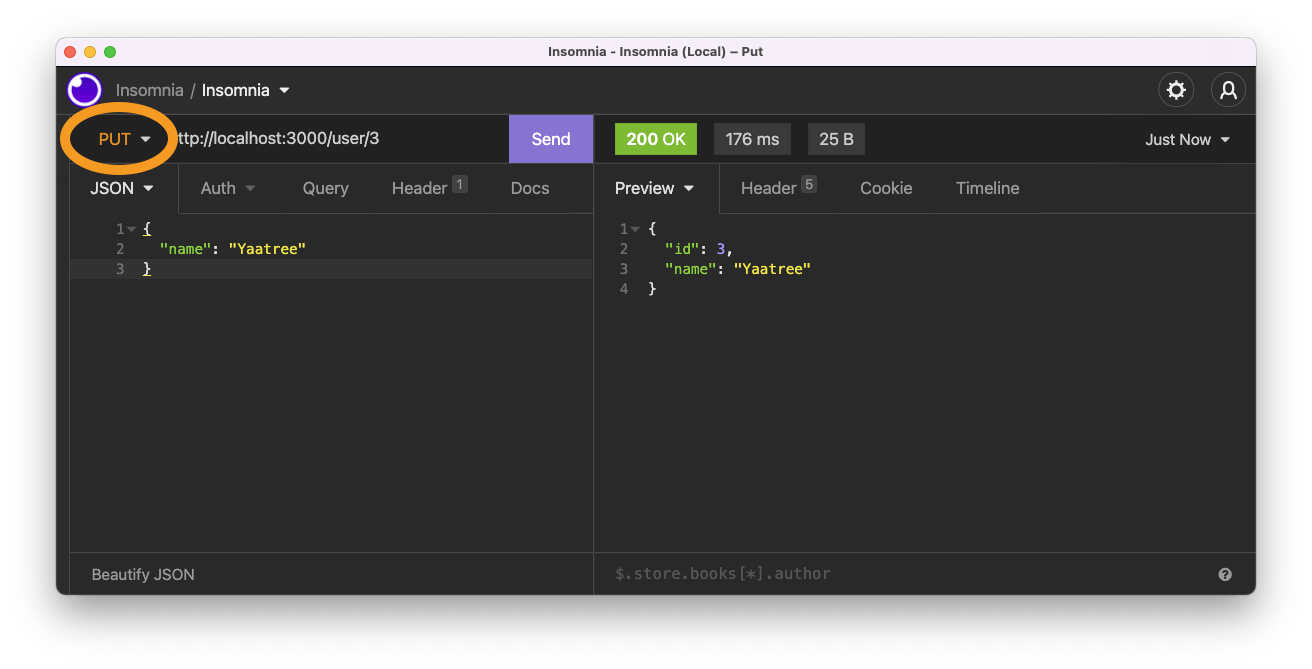
So the user with ID, which we just created, was chris, and now his name is Yaatree.
Deleting records
The last method we want to introduce is to delete records.
For this, we can leverage the DELETE request and send this to a specific ID.
The route will look like this:
app.delete <
{Params: IByIdParam} >
('/hobby/:id',
async (request, reply) => {
const {id} = request.params;
await prisma.hobby.delete({
where: {id: Number(id)},
});
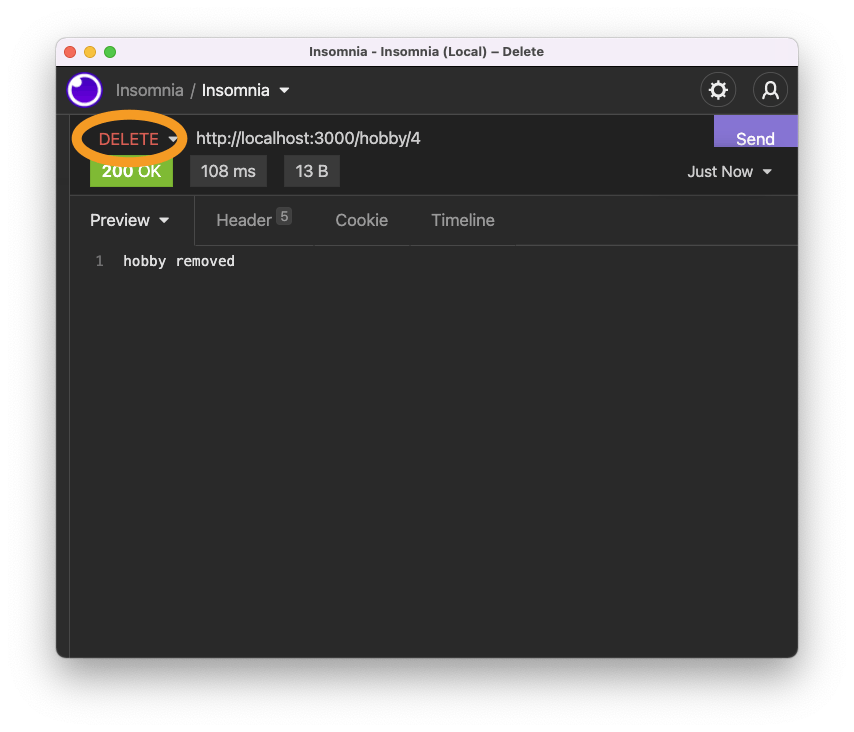
reply.send('hobby removed');
});
Here, we use the Prisma delete function to delete a specific hobby.
Then we reply with a string that the hobby has been removed.
Conclusion
And that's it. We now learned how to use CRUD operations with Fastify and Prisma. This is a. Super powerful combo, and you can create any web application with these two combined.
If you want to read the source code in detail, I've uploaded the project to GitHub.
Thank you for reading, and let's connect!
Thank you for reading my blog. Feel free to subscribe to my email newsletter and connect on Facebook or Twitter

